EV Charging Cable Safety and Security

Published: Thursday, 09 February 2023
Although safety & security might not be the main thing on your mind when buying an EV charger, it is definitely one of the most important aspects. Whether you’re buying a commercial or domestic EV charger, or you’re simply in need of a new cable, ensuring you’re using best practice while charging your EV cable means you shouldn’t come across any safety issues.
How do EV charging cables work?
Level 1 (120V) stations and a level 2 (240V) station provide pass-through C power from a power grid and safety earth ground to the electric vehicle for charging. The vehicle then converts this AC power to DC power used to recharge the batteries.
Although the actual “battery charger” is within the vehicle, an EVSE “charging station” implements several layers of safety features, to protect the user from electrical and fire hazards whilst both connecting and disconnecting to your car. Once connected to the vehicle, the station informs the user what charge is available throughout, and the vehicle takes over the power transfer.
If an electrical fault occurs, the EV charger should shut down immediately and the cable will be de-energised, minimising the risk of an accident.
EV security
How safe is EV charging with the right equipment?
Good news, when used correctly and when the right regulations are put in place, EV charging is extremely safe.
The National Electric Code (NEC) comes from the National Fire Protection Agency. This is a standard where buildings and equipment must meet minimum regulatory safety requirements in order to be safe enough for the general public to install and use. The NEC requires EV charging stations to be NRTL certified in order to be installed anywhere.
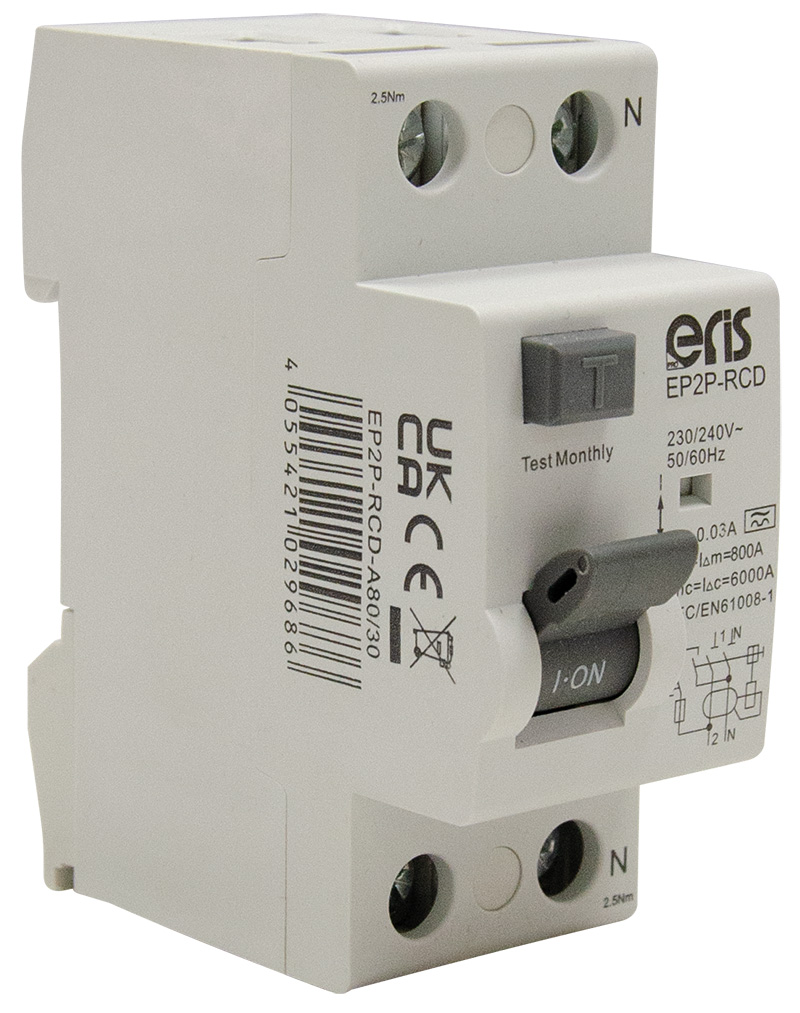
Does an EV charger need RCD protection?
Standing for ‘Residual Direct Current - Disconnecting Device’ a RDC-DD is often built within car charger equipment, in order to monitor and disconnect all live conductors if any DC problems appear on the C side of the installation.
If your car does not have this component, then you will need a Type B RCD supplying the car charger. This works effectively, as type B can detect this DC and still disconnect when required.

Should I unplug my EV cable when not in use?
A common concern amongst many electric car owners is leaving their EV charger plugged in while unattended. Experts strongly recommend looking through your owner's manual before acting on this decision, as different cars have different protocols.
For example, if you have a Tesla, the company site recommends that you keep the charger plugged in and set for 50% charge. On the other hand, if you have a Nissan Leaf, it is suggested that you leave your car unplugged as long as it is adequately charged; leaving it in for too long may drain the car's battery.
Do EV chargers need ventilation?
This depends on the type of EV charger and electric vehicle you have. It is important to check and confirm the car charger is properly tested and marked for indoor operation without ventilation. When ventilation is required, two holes should be drilled through the structure to provide both exhaust and fresh air make-up. Within this area, a dedicated fan and electrical circuit must be installed, and the fan and hole size must comply with the IAW NEC (National Electric Code).
This mechanical ventilation expels air, whilst also bringing in fresh air to ensure all gassing or fumes are expelled from the building.

Explore our range of EV charging cables
YESSS Electrical has a wide range of fully regulated and EV chargers for you to choose from, making electric vehicle safety a priority. We also have a wide selection of security systems for you to explore, adding an extra layer of security to your home EV charging. For friendly advice and enquiries, please contact our friendly experts.

